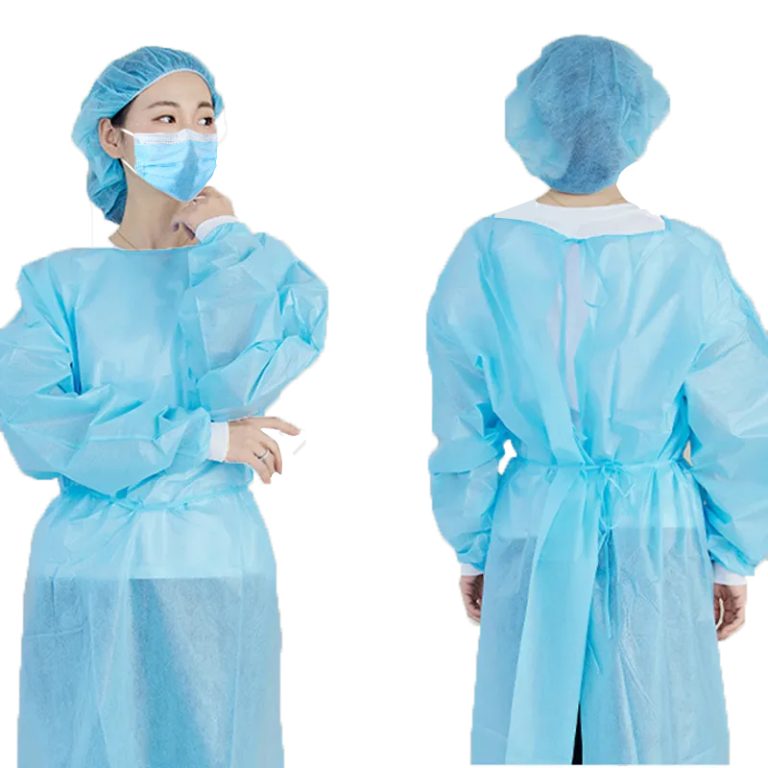
COVID-19 Protective Gowns: Types, Protection, and Safety for Workers
With the global spread of the COVID-19 pandemic, protective suits have become a vital personal protective equipment for medical staff and frontline workers, and their importance is increasingly evident. This article will delve into the types, design features, material selection, production standards, as well as usage and maintenance aspects of protective suits, in order to provide references for ensuring the safety of frontline workers engaged in the fight against the pandemic.
COVID-19 Protective Suit Overview
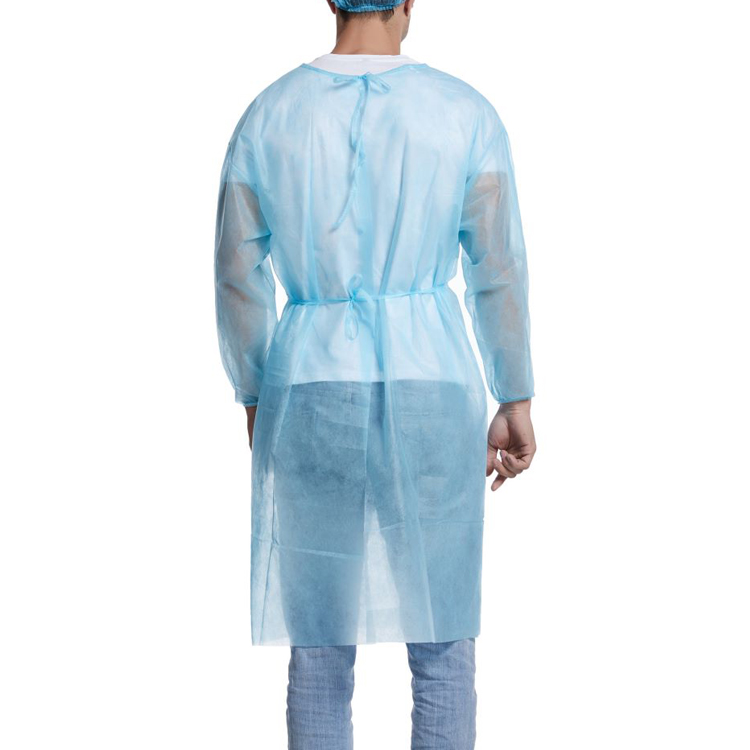
COVID-19 protective fits function the primary line of protection for healthcare employees and workers within the combat in opposition to the danger of novel coronavirus infection. these clothes are designed to isolate pathogens, lessen direct touch among healthcare employees and sufferers, and guard body of workers from contamination.
protecting suits are commonly built with a couple of layers, consisting of an outer water resistant layer, a middle filtration layer, and an internal moisture-wicking layer. The outer water-proof layer efficiently blocks liquid splashes, the middle filtration layer presents bacteria and virus filtration, and the internal moisture-wicking layer maintains consolation for the wearer.
In terms of structure, protective fits are available in sorts: complete-frame and separates. full-body fits provide fantastic sealability and ease of wear and tear, however might also impose sure limitations at the wearer’s mobility. Separates fits, along with separate tops and pants, are more appropriate for lengthy-duration paintings but require interest to the seamlessness between the pinnacle and pants.
In phrases of substances, typically used ones encompass polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). those substances no longer handiest own first-rate bodily homes which include waterproofing, oil resistance, and chemical resistance, however also have certain biocompatibility, ensuring they are harmless to the human body.
In phrases of manufacturing, the stitching of defensive suits calls for strict fine manipulate, mainly on the seams, which must be doubly or triply stitched to ensure no gaps are gift to prevent virus penetration. further, the rims, sleeve cuffs, and collars, which might be at risk of wear, want to be strengthened with special techniques to increase the lifespan of the suits.
earlier than use, healthcare people should cautiously look into the protective suits to make certain there are not any tears or infection. while wearing them, proper steps must be followed to keep away from infection for the duration of the donning and doffing procedure. After putting off the match, hand hygiene have to be done right now, and disposal should be performed in step with the policies.
COVID-19 protective fits play a essential role in the combat against the pandemic. They not only offer protection for healthcare workers however also act as a critical hyperlink in blocking the unfold of the virus. as the pandemic progresses, the nice and supply of shielding fits have grow to be a international issue.
To make sure the effectiveness of protecting fits, governments and health agencies around the arena have set up strict standards for their production and inspection. From raw fabric procurement to completed product manufacturing, each level calls for rigorous excellent control to ensure that every match can play its function at critical times.
As an vital device within the combat against the pandemic, the performance, high-quality, and supply of COVID-19 defensive fits have acquired unprecedented attention. With continuous technological improvements and the buildup of enjoy, the layout and manufacturing of protecting fits turns into more scientific and efficient, contributing to the worldwide combat towards the pandemic.
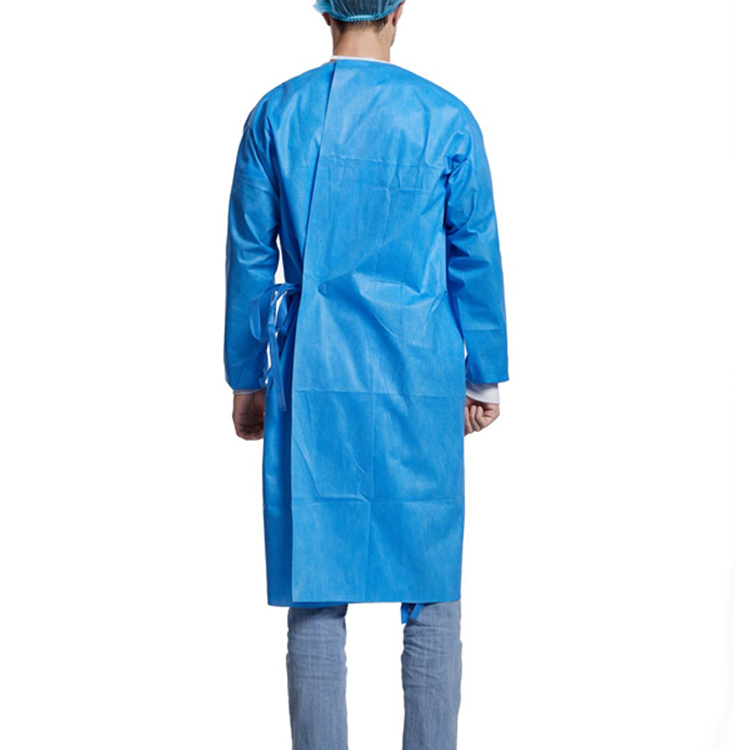

Protective suit functions and requirements
COVID-19 protective suits are an essential equipment for healthcare workers in the fight against the pandemic, with their primary functions including:
-
Preventing the Spread of the Virus: The primary role of protective suits is to prevent the transmission of the virus through airborne droplets, contact, and other means. Their design is intended to provide the wearer with a sealed protective space, minimizing the possibility of viral penetration.
-
Protection against Air Pollution: In areas with high levels of virus activity, the air may contain a significant amount of viral particles. Protective suits effectively block these particles, protecting healthcare workers from air pollution.
-
Protection of the Healthcare Workers’ Skin: Prolonged contact with patients or medical equipment can lead to skin damage. Protective suits, made from breathable materials, reduce direct contact with the external environment, thereby lowering the risk of skin damage.
-
Adaptability to Various Work Environments: Protective suits must be adaptable to different work settings, such as wards and isolation areas. Their design should consider the wearer’s comfort to ensure that healthcare workers remain unfatigued during long shifts.
-
Compliance with Hygiene Standards: Protective suits must have good impermeability to prevent patient body fluids, blood, and other contaminants from penetrating. Additionally, the material should be easy to clean and disinfect, ensuring the hygiene and safety of the suits during reuse.
-
Adaptability to Different Body Types: To meet the needs of healthcare workers of various body types, protective suits must have good elasticity and adaptability. They should also ensure that the wearer is not restricted in movement, thus enhancing work efficiency.
-
Field of Vision and Range of Motion: The design of protective suits must balance the wearer’s field of vision and range of motion, ensuring that healthcare workers can clearly observe patients and perform necessary treatments.
-
Material Safety: The materials used in protective suits must meet national standards to ensure they are harmless to the human body. Especially during the pandemic, the safety of the material is particularly important as healthcare workers wear them for extended periods.
-
Easy to Disassemble and Replace: The design of protective suits should facilitate quick disassembly and replacement by healthcare workers to respond to emergencies.
-
Easy Storage and Transportation: To facilitate use in different locations, protective suits must have good storage and transportation properties, ensuring they can be quickly deployed in emergencies.
In summary, the functions and requirements of COVID-19 protective suits encompass a wide range of aspects, including protection against viral infection, prevention of air pollution, increased work efficiency, comfort for the wearer, compliance with hygiene standards, adaptability to different body types, and more. The realization of these functions and requirements is of great significance in improving the safety coefficient and treatment effectiveness of healthcare workers in the fight against the pandemic.
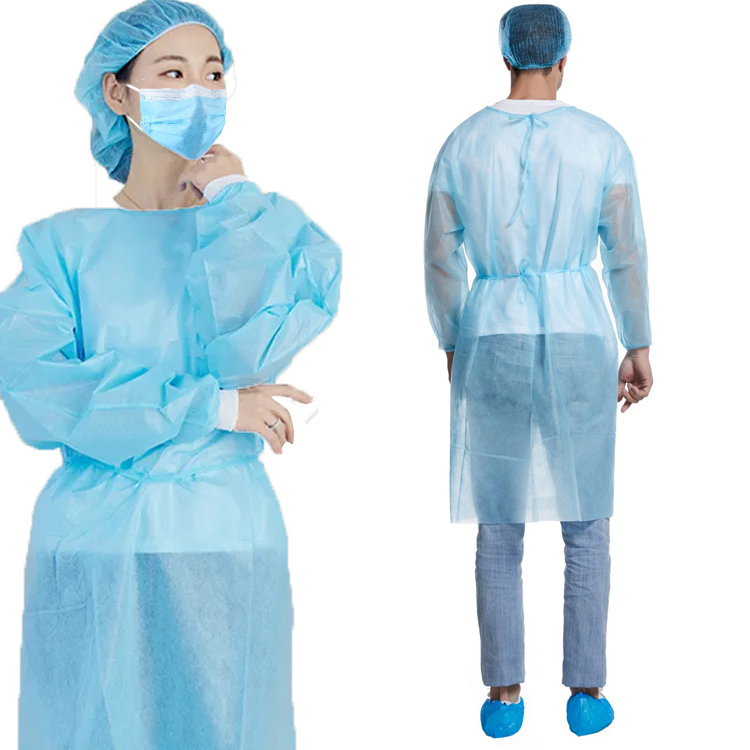
Types and Design Features of Protective Clothing
Protective suits can be categorized based on their usage and protective levels, and the following are several common types along with their design features:
-
Protective Suit Material: Common materials for protective suits include polyethylene (PE) and polypropylene (PP), which have good properties of waterproofing, dust-proofing, and virus barrier. The design takes into account the thickness of the material according to the protective requirements to ensure sufficient protection.
-
Dissectible Protective Suits: Dissectible protective suits consist of separate parts such as the jacket, pants, hat, gloves, and boot covers. The design emphasizes the coordination of these components to ensure that the wearer is not constrained during movement. The jacket and pants are connected with a zipper for easy donning and doffing, while also preventing contamination.
-
Full-body Protective Suits: Full-body protective suits are designed with an integrated structure for the jacket, pants, hat, gloves, and other components. The overall structure is compact, effectively preventing viruses in the air from entering through gaps. The design emphasizes sealing, often using adhesive or stitching techniques to ensure no gaps.
-
Comfort: When designing protective suits, consideration is given to the wearer’s need for long-term wear. Soft, breathable materials are used to reduce skin friction and sweating. The design of pockets, zippers, and other areas is also optimized for convenience.
-
Protective Level: Protective suits are categorized into levels such as level one, level two, and level three, with higher levels indicating stronger protective performance. The design takes into account the actual working environment and the types of viruses that may be encountered, choosing the appropriate level of protective suit. For example, in environments with a high risk of infection, level three protective suits should be chosen.
-
Protective Suit Identification: Protective suits usually have markings indicating the protective level, material, production date, manufacturer, and other information for easy identification by users. The design ensures that the markings are clear and visible for quick identification in emergencies.
-
Protective Suit Accessories: Depending on the actual needs, protective suits can be equipped with various accessories such as goggles, face masks, and respirators. The design considers the compatibility and stability of the accessories to ensure that they do not become loose or fall off during wear.
-
Sterilization: To improve the hygiene standards of protective suits, sterilization is considered in the design. Methods such as high-temperature steam and ethylene oxide are commonly used to sterilize the suits to ensure that the wearer is not contaminated by bacteria or viruses during use.
-
Portability: The design of protective suits takes into account the possibility that wearers may need to carry other tools or items, so the clothing is designed for portability. This includes using lightweight materials to reduce weight and make it easier for the wearer to carry.
-
Adaptability: The design of protective suits should have strong adaptability to fit wearers of different body types and heights. The design offers various sizes to ensure that each wearer can find a suitable fit.

Material Selection and Process Standards
The choice of material for protective suits is crucial, as it directly affects their protective performance and the comfort of the wearer. The following is a detailed description of the material selection and manufacturing standards:
-
Fabric Selection: The fabric of the protective suit must have excellent barrier properties to effectively prevent the penetration of viruses and bacteria. Common materials include polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). PE and PP materials are lightweight and cost-effective, but their barrier properties are relatively weaker; PTFE materials, on the other hand, offer excellent resistance to penetration, although they are more expensive.
-
Waterproofing: In the case of COVID-19 and other viruses, the protective suit needs to have certain waterproof properties to prevent the splashing of droplets and liquids. This is generally achieved through the use of waterproof coatings or special fiber materials. Waterproof coatings should have good durability and be resistant to peeling.
-
Flame Retardancy: During the manufacturing process, the flame retardant properties of the protective suit should be considered to prevent harm in the event of a fire. Flame retardants are typically applied to the fabric to make it less flammable.
-
Breathability: Long-term wearing of protective suits makes breathability a key factor affecting the wearer’s comfort. The protective suit should have a certain level of breathability to ensure internal air circulation. Fabrics with good breathability often use multi-layer composite structures, such as nanofibers and microporous membranes.
-
Antimicrobial Properties: To prevent the growth of viruses on the surface of the protective suit, the fabric should have certain antimicrobial properties. Common antimicrobial materials include silver ions and copper ions, which effectively inhibit the growth of bacteria and viruses.
-
Manufacturing Standards:
a. Adhesive Bonding: The choice of adhesive and its application during the manufacturing process of the protective suit is very important. Environmentally friendly, non-toxic, and high-temperature-resistant adhesives should be used to ensure the integrity and stability of the protective suit.
b. Welding: For areas that require sealing, such as necklines and sleeve cuffs, welding can ensure the sealing integrity of the protective suit and prevent the penetration of viruses.
c. Sewing: The sewing process should be rigorous to avoid issues such as thread breakage and exposed seams. The ends of the sewing threads should be flat-ironed to ensure the neatness and aesthetics of the protective suit.
d. Surface Treatment: Before the protective suit is shipped, the surface should be treated for flatness and burr removal to ensure the comfort and service life of the suit.
e. Quality Inspection: The protective suit should undergo strict quality inspections during the manufacturing process to ensure that its performance indicators meet national and industry standards.
Through strict control over material selection and manufacturing standards, the effective protective capabilities of protective suits during the fight against COVID-19 and other viruses can be ensured, providing safety guarantees for medical staff and epidemic prevention workers.
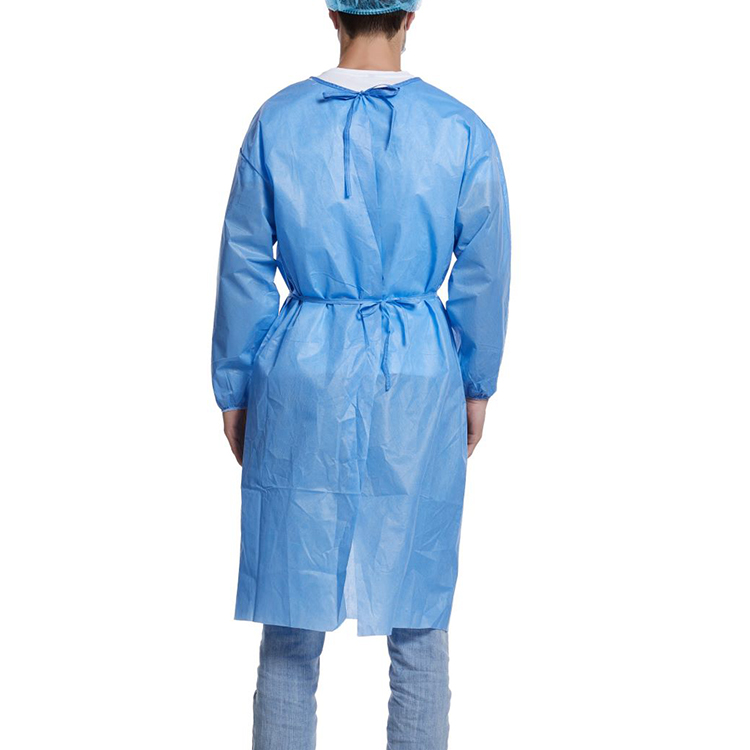

User and Maintenance Manual
When using protective suits, it is necessary to strictly follow the following steps:
-
Proper Dressing: Before wearing the protective suit, ensure that your hands are clean and avoid direct contact with your face. First, wear a medical mask, then grasp the bottom hem of the protective suit with both hands and pull it over your head, ensuring that your face is completely covered. Pull the bottom hem down to the waist and adjust the elastic to a comfortable fit.
-
Disposal of Protective Suits: When removing the protective suit, avoid contaminating the inner layer. First, remove the mask, being careful not to touch the outer surface. Then, hold the collar of the protective suit with one hand and the collar below it with the other, flipping the suit to the front of your body. Extend your hands through the sleeve openings and quickly remove the suit, avoiding contact with your face and head.
-
Use of Gloves: When wearing gloves, ensure that your hands are clean. Put on the gloves and adjust the length to a suitable size. When removing gloves, turn them inside out to avoid contaminating the outer surface, and dispose of them immediately or disinfect them.
-
Cleaning of Protective Suits: Place the removed protective suits in a designated area, avoiding contact with other items. If possible, use a chlorine-based disinfectant to disinfect the protective suits.
-
Skin Protection: When in contact with items or environments that may contain viruses, wear a protective suit and also maintain clean skin, avoiding direct contact.
-
Routine Maintenance: Regularly clean and disinfect the protective suits after use. When washing, use a neutral detergent and lukewarm water, avoiding the use of bleaches or other irritant chemicals. For disinfection, you can choose a chlorine-based disinfectant or an ultraviolet disinfection device.
-
Storage Requirements: Fold the protective suits neatly when storing them to avoid damaging the protective layers. The storage area should be well-ventilated and dry.
-
Personal Hygiene: When wearing protective suits, pay attention to personal hygiene and avoid touching your face. If possible, wear goggles or a face shield for additional eye protection.
-
Respiratory Protection: When in contact with air that may contain viruses, wear a medical mask or N95 mask to ensure respiratory safety.
-
Information Recording: During the use of protective suits, record information such as the items contacted, time, and location, for traceability and investigation purposes.
Following these guidelines for use and maintenance can effectively ensure the effectiveness of the protective suits and reduce the risk of infection.
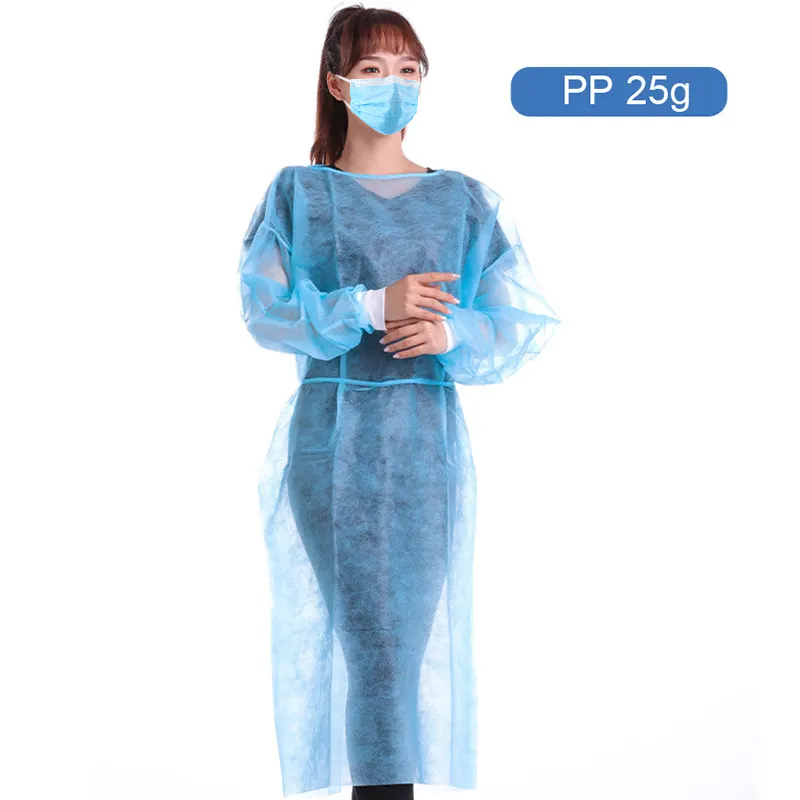

Protective suits in the role of epidemic prevention and control
Protective suits play a crucial role in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic, serving multiple functions in various aspects:
Effectively blocking the spread of the virus: Protective suits effectively shield against droplets and aerosols that may carry the virus, reducing the risk of transmission through direct contact or airborne routes.
Protecting healthcare workers: During the COVID-19 crisis, healthcare workers are the most directly exposed to the virus threat. The protective suits provide them with isolation protection, lowering the risk of infection and ensuring the smooth conduct of medical work.
Reducing cross-infection: The use of protective suits in medical institutions and quarantine sites helps reduce cross-infection between patients and healthcare workers, as well as among patients themselves.
Maintaining normal medical order: During the peak of the pandemic, the availability of protective suits directly impacts the operation of medical institutions. Effective protective measures help healthcare workers work with peace of mind, maintaining the normal order of medical care.
Enhancing public confidence: As an important material in the fight against the pandemic, the sufficient supply and standardized use of protective suits can boost public confidence in the COVID-19 control efforts.
Improving the efficiency of control measures: The use of protective suits helps enhance the efficiency of pandemic control, ensuring that all preventive measures are effectively implemented.
Strengthening the effect of isolation: In quarantine sites, the wearing of protective suits is an essential part of the isolation measures, helping to prevent the spread of the virus within the isolation area.
Promoting international cooperation: During the pandemic, sharing protective suits and other medical supplies among countries aids in joint efforts to combat the challenge of the virus, fostering international cooperation and support.
In summary, protective suits play a multifaceted role in pandemic control, from protecting healthcare workers and reducing cross-infection to maintaining medical order and enhancing public confidence. Their importance is self-evident. In future pandemic control efforts, protective suits will continue to play a critical role.
Sure, here is the translation:Conclusion
Protective suits play a crucial role in the fight against the COVID-19 pandemic, and their specific functions are described as follows:
-
Isolation of Virus Transmission: As essential equipment for medical staff and frontline workers, protective suits effectively isolate the virus, preventing its spread through respiratory routes, bodily fluids, and other means, thereby reducing the risk of infection.
-
Protection of Medical Personnel: During periods of high virus prevalence, medical staff are the vanguard in the fight against the pandemic. Protective suits provide necessary protection for healthcare workers, reducing the chance of direct contact with patients and lowering the risk of infection.
-
Ensuring Medical Safety: The use of protective suits helps maintain a clean medical environment and reduces the likelihood of cross-infection, ensuring the smooth progress of medical work.
-
Enhancing Work Efficiency: In the context of pandemic response, medical staff often work for extended periods. The design of protective suits, considering both comfort and ease of use, aids in improving efficiency and reducing fatigue caused by discomfort.
-
Strengthening Public Confidence: The widespread use and standardized application of protective suits demonstrate the country’s high priority in pandemic control, helping to boost public confidence in the fight against the virus.
-
Promoting Global Cooperation: In the face of the global spread of the pandemic, protective suits serve as important materials for international aid, strengthening cooperation between countries in the fight against the virus and addressing common challenges.
-
Advancing Medical Technology: The design and production of protective suits during the pandemic have propelled the advancement of related medical technologies, providing valuable experience for future responses to similar public health emergencies.
-
Raising Public Health Awareness: The widespread use and promotion of protective suits have increased public awareness of pandemic control, contributing to the enhancement of public health consciousness and fostering a positive atmosphere of societal participation.
-
Promoting Rational Allocation of Medical Resources: During the early stages of the pandemic, there was a shortage of medical supplies such as protective suits. Rational allocation and use of these suits helped alleviate the tension in medical resources.
-
Reflecting National Emergency Response Capabilities: The production and supply of protective suits during the pandemic reflect the country’s emergency response capabilities in dealing with public health emergencies, showcasing the comprehensive national strength.
In summary, protective suits play a significant role in pandemic control, not only protecting medical staff and patients but also enhancing public health awareness and promoting global cooperation in the fight against the virus. In the future, we should continue to focus on the research and production of protective suits to prepare for various public health emergencies.