Hospital Workwear Suit: Ideal for Hospital Doctor Uniforms
in the scientific enterprise, the medical doctor’s uniform is not most effective a symbol of expert identity however also embodies functionality, safety, standardization, and diversity. this newsletter will discover the shade coordination of clinic doctors’ uniforms and the profound symbolic meanings they create.
Design Principles for Hospital Doctor Workwear
The design principles for hospital doctor uniforms are aimed at ensuring that the clothing meets the special requirements of the medical environment while also reflecting the professional image of medical staff. The following is a specific description of these design principles:
-
Functionality and Practicality: The design of the uniforms must prioritize practicality, allowing doctors to move freely in the stressful work environment. Details such as sleeve openings, necklines, and pockets should be designed with ease of operation and storage needs in mind.
-
Hygiene Requirements: Considering the hygiene standards of the hospital environment, the fabric of the uniforms should possess properties such as ease of cleaning, static resistance, and antibacterial properties to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
-
Safety Protection: The design of the clothing should include safety features for the protection of doctors’ occupational health, such as liquid-proof and sharp-object-resistant designs, while also considering the protection of patients from potential harm.
-
Professional Image: The color, style, and details of the uniforms should convey the professionalism and authority of medical staff, typically using white or light blue tones to represent purity and trust.
-
Adaptability to Different Departments: The design of the uniforms for doctors in different departments should consider the unique characteristics and departmental culture of each, such as surgical uniforms may emphasize sterility and protection, while pediatrician uniforms may be more warm and friendly.
-
Comfort: The design of the uniforms should take into account the need for doctors to wear them for long periods, using soft, breathable materials to minimize discomfort.
-
Identification: The uniforms should have clear departmental identification and doctor names to facilitate patient recognition, enhancing the transparency and trust in medical services.
-
Ease of Identification and Management: The design of the uniforms should facilitate identification and management, such as distinguishing different levels of doctors through color and making it convenient for cleaning and disinfection.
-
Longevity and Durability: Considering that the uniforms need to be washed and replaced frequently, the design should choose durable materials to ensure that the uniforms maintain good condition over long-term use.
-
Personalization and Fashion: On the basis of maintaining professionalism, appropriate personalization should be incorporated into the design, making the uniforms both practical and stylish, enhancing the professional pride of medical staff.
In summary, the design principles for hospital doctor uniforms encompass aspects such as functionality, safety, professionalism, comfort, and practicality, aiming to provide medical staff with an environment that meets their work needs while also showcasing their professional image.
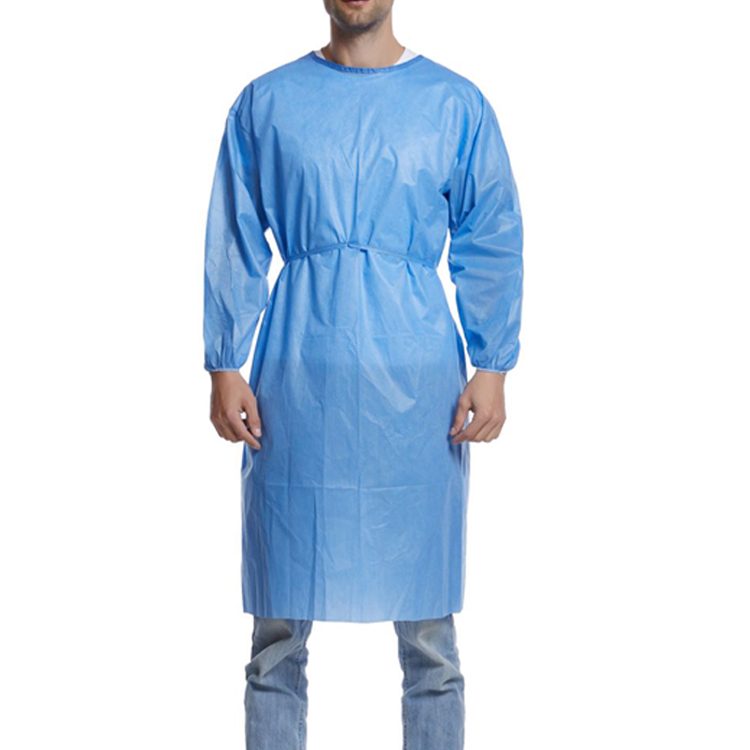

Functionality and safety of hospital workwear
Hospital work uniforms prioritize functionality and safety as the two core elements in their design. The following descriptions detail these aspects:
-
Antimicrobial and Antipollution: Hospital work uniforms are made from special fabrics, such as the combination of polyester fibers with nanotechnology, which effectively resist the attachment of bacteria and viruses, reducing the risk of cross-infection. The surface treatment of the fabric makes stains difficult to penetrate, facilitating cleaning and disinfection.
-
Protective Function: The design of the uniforms takes into account the protective needs of doctors during surgeries or when in contact with patients. For example, surgical gowns have a double-layer structure, with the inner layer made of liquid-proof materials and the outer layer of easily cleanable fabric, to prevent direct contact with pollutants such as blood and body fluids.
-
Breathability: The materials used in hospital work uniforms typically have good breathability, ensuring that the wearer remains dry during long shifts, reducing discomfort caused by sweating.
-
Comfort: The design of the uniforms focuses on ergonomics, with a well-fitted cut to minimize. The sleeves and necklines have adjustable designs for comfort adjustments during various operations.
-
Easy to Put On and Take Off: The uniform has designed pockets for carrying medical tools and documents. Additionally, the sleeves and necklines are designed for quick donning and doffing, improving work efficiency.
-
Visibility: The color and pattern design of the uniforms are identifiable, such as white or light-colored, making it easy for patients to recognize the identity of the doctors. Moreover, some uniforms have prominent hospital logos on the sleeves, necklines, or chest, enhancing safety.
-
Antistatic: Hospital work uniforms are made from antistatic fabrics to reduce the risk of sparks caused by static electricity, lowering the fire hazard.
-
Hypoallergenic: Considering the health of both patients and doctors, the fabric choices avoid substances that can cause allergies, such as formaldehyde and heavy metals.
-
Durable: The uniforms are made from materials that are wear-resistant, able to withstand frequent washing and wearing, and extend the service life.
-
Environmental Protection: The production process of the uniforms adheres to environmental standards, reducing environmental impact and aligns with the concept of sustainable development.
In summary, the functionality and safety of hospital work uniforms are reflected in multiple aspects, from fabric selection to design details, all aimed at providing doctors with a comfortable, safe, and convenient work experience, while also ensuring the environmental and health safety of patients and hospitals.
Standardization and Diversity in Hospital Workwear
The standardization of hospital uniforms is reflected in their uniformity, standardization, and practicality. Firstly, unified dress codes help enhance the overall image of the hospital, boost the service awareness of medical staff, and strengthen team cohesion. Secondly, the standardized design ensures the uniformity of functionality, such as pocket placement and zipper design, making it convenient for medical staff to carry essential items.
Diversity is evident in the styles, colors, and materials of the uniforms. In terms of styles, according to the needs of different departments and positions, there are various choices, such as long-sleeve, short-sleeve, and overall designs. In terms of colors, usually white, blue, green, and other colors are used, which are easy to clean and have high visibility. In terms of materials, hospital uniforms need to combine comfort and durability, such as cotton and blended fabrics, to meet the needs of different seasons and working environments.
Specifically, the following are several aspects of standardization and diversity:
-
Standardized Color: Hospital uniforms typically use basic colors such as white, blue, and green, which are not only easy to clean but also visually create a fresh medical atmosphere. Standardized color use also facilitates the identification and distinction of different departments among patients.
-
Standardized Styles: The design of uniform styles follows ergonomics principles to ensure comfort and ease of movement. For example, nurse uniforms are designed with a loose fit to facilitate movement for nurses during operations; doctors’ white coats are often designed in a straight or slightly fitted style for ease of walking and treatment.
-
Diverse Materials: Depending on the season and regional characteristics, hospital uniforms are made of different materials. For summer, breathable cotton fabrics can be chosen, while for winter, warm blended fabrics are used. In addition, special materials for specific departments, such as operating rooms and infectious disease units, may be required to ensure the safety of medical staff and patients.
-
Diverse Styles: For different positions, hospital uniforms come in various styles. For example, nurse uniforms have long-sleeve, short-sleeve, and overall options, while doctor’s white coats come in styles such as single-breasted, double-breasted, and without buttons. Furthermore, some uniforms are designed with name tags or epaulettes to distinguish different departments and positions.
-
Standardized Identification: Hospital uniforms usually feature the hospital name, department name, position information, etc., for easy identification by patients and for communication among medical staff. The design of the identification also follows standardized principles to ensure clarity and readability.
The combination of standardization and diversity in hospital uniforms meets the demands of hospital image and functionality, while also considering the convenience and comfort of medical staff.
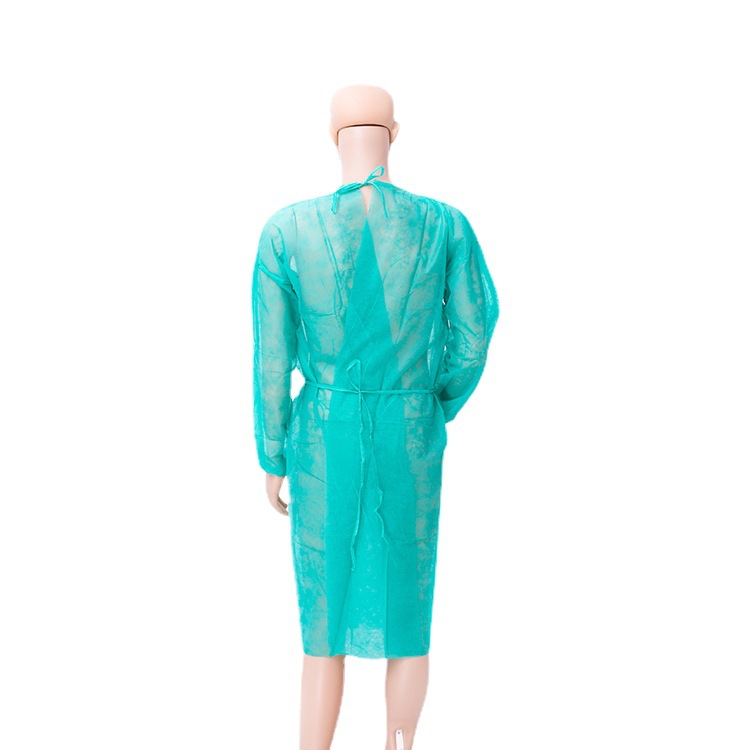

Material Selection for Hospital Doctors’ Workwear
-
Cotton: Cotton materials are favored for their excellent breathability and moisture-wicking properties. They provide medical staff with a comfortable working environment, reducing physical discomfort caused by long hours of work. Cotton workwear is soft and skin-friendly, helping to alleviate work-related stress.
-
Nylon: Nylon is known for its high abrasion resistance and tear resistance, making it suitable for work environments that involve frequent wear and washing. It can withstand the of oils and chemicals, maintaining the cleanliness and hygiene of the workwear.
-
Polyester: Polyester offers excellent elasticity, is resistant to deformation, and is ideal for tailoring well-fitting workwear. This material is easy to clean and dry, suitable for quick changes to reduce the risk of cross-contamination.
-
Polyurethane (PU) or Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): These materials are commonly used to make protective garments such as isolation gowns and surgical suits. They have the characteristics of preventing liquid penetration, withstanding high temperatures, and resisting chemical corrosion, ensuring the safety of medical staff during specific operations.
-
Polyester: Lightweight and easy to maintain, polyester is resistant to pilling and suitable for making daily workwear. It has good thermal properties, providing warmth for medical staff, especially in cold climates.
-
Cotton-Polyester Blends: Combining the comfort and breathability of cotton with the durability and wrinkle resistance of polyester, cotton-polyester blended workwear maintains the comfort of cotton while offering the toughness of polyester, making it a common material for hospital workwear.
-
Antimicrobial Materials: With the continuous development of the medical industry, antimicrobial materials are increasingly being used in the production of workwear. These materials can inhibit the growth of bacteria, reducing the risk of hospital-acquired infections.
When selecting the material for hospital doctor workwear, the following factors should also be considered:
-
Color: The color of the workwear should be easy to clean, facilitate the distinction between different roles of medical staff, and also align with the overall image of the hospital.
-
Size: The size of the workwear should fit staff of various body types, ensuring comfort and not hindering work efficiency.
-
Design: The design of the workwear should be simple and elegant, in line with the professional image of the medical industry, and convenient for medical staff to move around in a busy working environment.
The choice of material for hospital doctor workwear should meet functional requirements while also considering the comfort and safety of the medical staff. Through reasonable pairing, provide practical and aesthetically pleasing workwear for medical staff.
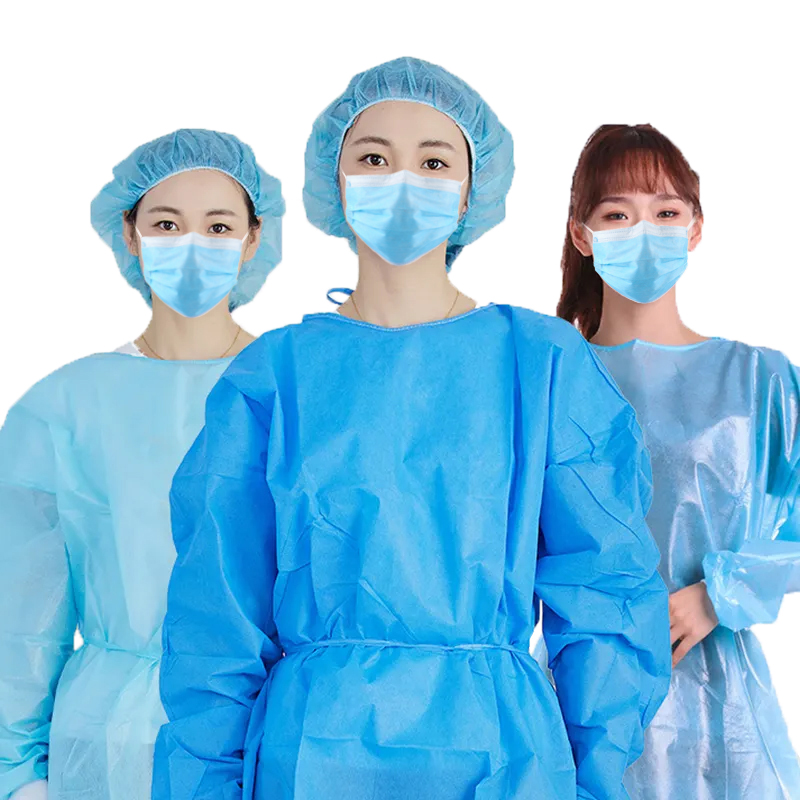

Color Matching and Symbolic Meanings of Hospital Workwear
The color coordination of hospital uniforms typically adheres to the following principles:
-
Professionalism of the medical environment: The color choice for hospital uniforms is often subdued and solemn, with dark blue, white, and gray being favored. Dark blue conveys a sense of professionalism and calmness, while white represents purity and cleanliness. Gray combines the characteristics of both, appearing professional and easy to clean.
-
Symbol of doctors’ authority: In terms of color selection, red and gold are commonly used in the detail decorations of doctors’ uniforms. Red symbolizes passion and vitality, representing the spirit of doctors saving lives and healing injuries; gold gives a sense of authority and nobility, reflecting the professional status of doctors.
-
Identification of departmental distinction: Different departments’ uniforms are distinguished in color to facilitate recognition among patients and colleagues. For example, surgeons’ uniforms may be predominantly green, as green psychologically brings a sense of relaxation and trust; pediatricians’ uniforms may be in pink or blue, with pink representing gentleness and blue representing tranquility, suitable for the warm atmosphere of pediatrics.
-
Comfort of color: The material and color of the uniform should take into account the comfort of the wearer. Soft, breathable fabrics paired with suitable colors not only help alleviate fatigue from long hours of work but also enhance the mood of the wearer.
-
Reflection of hospital culture: The color of hospital uniforms also reflects the hospital’s values and cultural characteristics. Some hospitals may choose colors with regional characteristics, such as using specific colors to reflect regional characteristics and cultural heritage.
-
Strengthening symbolic meaning: In color coordination, black is often used to emphasize seriousness and authority, suitable as the main color of hospital uniforms. White is used to emphasize cleanliness and hygiene, which is an indispensable element in the medical environment.
-
Environmental protection and sustainability: With the rise of environmental awareness, the color selection of hospital uniforms is also increasingly focusing on environmental protection and sustainability. Using natural fibers such as cotton and linen is not only beneficial to human health but also in line with the green medical concept.
-
Coordination and harmony of colors: The color coordination of hospital uniforms should avoid being too bright or dazzling, which may affect the mood of patients. Overall, the color coordination should aim for harmony and coordination, neither too monotonous nor too flashy.
In summary, the color coordination of hospital uniforms is closely linked to their symbolic meanings, reflecting the professionalism and authority of the medical industry, meeting the needs of patients and medical staff, and also reflecting the values and cultural connotations of the hospital.






