Lab Coat Essentials: The Ultimate Guide for Researchers Protective Gear
Laboratory coats, as an integral defensive gear for researchers in their every day paintings, directly have an effect on the accuracy of experiments and the health and safety of personnel. With the non-stop enlargement and refinement of the scientific research field, Lab Coats are more and more applied in diverse domain names. this article will talk precise utility times of Lab Coats in fields such as scientific studies, prescription drugs, and biotechnology. moreover, the article will offer sensible pointers for the cleaning and maintenance of Lab Coats. sooner or later, we can analyze the improvement developments and market prospects of Lab Coats, aiming to provide reference for associated organisations and researchers.
The functions and importance of laboratory uniforms
Laboratory coats, as an essential equipment for researchers during the experimental process, serve multiple functions and their importance is self-evident. The following will elaborate on the functions and importance of laboratory coats from several aspects.
Laboratory coats effectively prevent direct contact between experimenters and chemical substances or biological samples. In chemical experiments, experimenters may come into contact with corrosive, irritant, or harmful chemicals, and wearing specialized protective clothing can reduce the harm to the skin from these substances. In biological laboratories, avoiding cross-contamination from biological samples is equally crucial. Professional protective clothing is designed with properties to prevent penetration and splashing, ensuring the safety of both the experimenter and the environment.
Laboratory coats also have excellent fire-resistant properties. In high-temperature or flammable and explosive environments, the clothing provides sufficient protection to prevent injury from flames or high temperatures. This protective characteristic is particularly important in fields such as materials science and new energy research.
Laboratory coats also excel in physical protection. During experiments, there may be situations such as broken glassware or high-temperature splashes from metal objects. Wearing standard protective clothing can prevent these physical injuries to some extent.
The design of laboratory coats takes into account the special environment of the laboratory. The material of the clothing usually has anti-static and easy-to-clean properties, which help maintain the cleanliness of the experimental environment and reduce sources of contamination. For experimenters who need to wear them for extended periods, comfortable design is also a crucial factor, reducing discomfort from prolonged work.
In terms of detailed design, such as the cuffs, collars, and hem of the laboratory coats, there are usually tightening devices to prevent accidental leakage of liquids or powders during experiments. In addition, some work clothes are equipped with special pockets for convenient storage of experimental tools and records.
The importance of laboratory coats is also reflected in the following aspects:
-
Ensuring the accuracy of experimental data: By avoiding the influence of experimenter factors (such as skin allergies, sweat secretion, etc.) on the experimental results, it ensures the accuracy and reliability of the experimental data.
-
Improving work efficiency: Wearing appropriate work clothes allows experimenters to focus more on experimental operations, thereby improving work efficiency.
-
Reducing safety accidents: By providing necessary protection, it reduces the risk of safety accidents during the experiment.
-
Establishing a professional image: Standardized laboratory coats help establish a good image of research institutions, enhancing the overall level of scientific research.
The role of laboratory coats in scientific research is indispensable. They not only provide safety for experimenters but also help improve experimental efficiency and the quality of scientific research. Therefore, choosing the right work clothes is crucial for laboratory workers.

Selecting Material for Laboratory Protective Clothing
-
Polyester Fiber: Polyester fibers possess excellent chemical resistance, are not easily corroded, and have high heat resistance. This material is lightweight and breathable, often used to make routine laboratory protective clothing, such as lab white coats.
-
Nylon: Nylon material boasts superior wear resistance and elasticity, is lightweight, and has good resistance to water and oil. Nylon protective suits are widely used in chemical laboratories and are suitable for protecting against corrosive liquids and oils.
-
Acetate Fiber: Acetate fibers have high strength and toughness, good resistance to acids and alkalis, and are suitable for contact with corrosive substances such as strong acids and alkalis. However, acetate fibers are prone to moisture absorption, which may cause skin discomfort if worn for extended periods.
-
Polyurethane: Polyurethane material has outstanding resistance to chemicals and can withstand the of various solvents, acids, and alkalis. Polyurethane protective suits are suitable for high-risk chemical experiments such as organic synthesis and drug research.
-
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE): Also known as Teflon, PTFE has excellent chemical and high-temperature resistance and does not react with almost any chemicals. PTFE protective suits are suitable for extreme chemical experiment environments, such as nuclear reactors.
-
Antistatic Materials: In environments prone to fire and explosion, antistatic protective suits effectively prevent the generation of static electricity, avoiding accidents caused by sparks. This type of material is usually made from a special blend of fibers with good conductivity.
-
Waterproof and Breathable Materials: For laboratory personnel engaged in liquid operations or working in a moist environment for extended periods, waterproof and breathable protective suits are an ideal choice. These suits effectively prevent moisture penetration while maintaining good breathability.
-
Antimicrobial Materials: In biological laboratories, hospitals, and other facilities, it is crucial to choose protective suits made from antimicrobial materials to prevent cross-contamination. These materials usually contain antimicrobial agents that can inhibit the growth of bacteria.
When selecting the material for laboratory protective clothing, the following factors should be considered:
- Laboratory Environment: Choose materials with corresponding protective properties based on the nature of the experiment.
- Experimental Substances: Select materials with good chemical resistance for different corrosive chemicals.
- Duration of Work: For protective suits worn for long periods, choose materials that are breathable and comfortable.
- Comfort: The material should be soft and skin-friendly to reduce discomfort during wear.
- Economic Costs: Consider cost factors while meeting protective requirements.
The selection of materials for laboratory protective clothing should take into account factors such as laboratory environment, experimental substances, duration of work, comfort, and economic costs to ensure the safety of laboratory personnel.

Design Standards and Features of Lab Coats
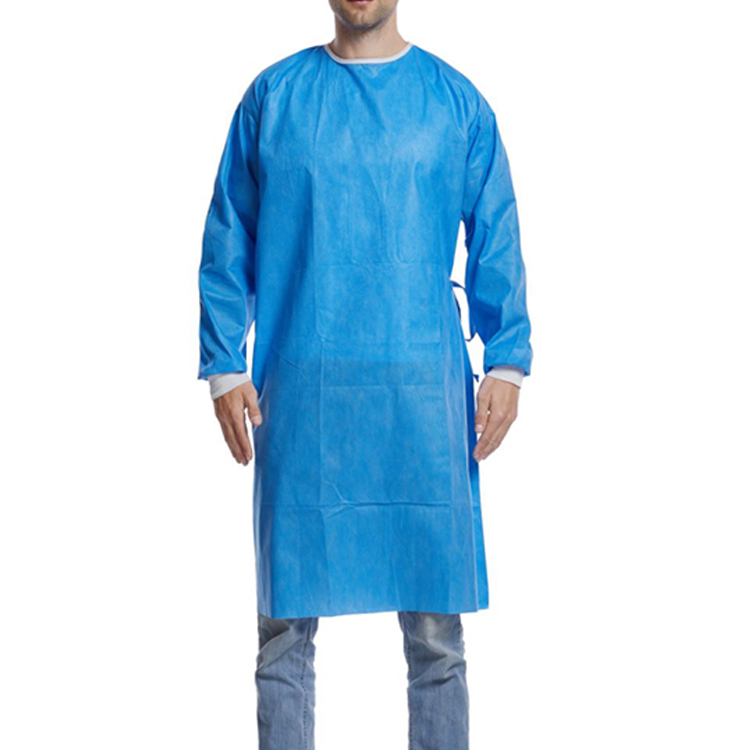
In terms of fabric selection, Lab Coats typically use materials that are waterproof, resistant to chemicals, and heat-resistant, such as polyester, polypropylene, and PVC, among others. These materials ensure that laboratory personnel receive effective protection when in contact with chemical substances, biological samples, or during high-temperature experiments.
In terms of design, Lab Coats feature a simple and practical style, adhering to the principle of loose and comfortable fit. The front door design facilitates easy on and off, while the back opening design allows for greater freedom of movement. The sleeve cuffs and waist are equipped with elastic bands to ensure a snug fit and prevent the entry of liquids or particulate matter.
In terms of color, Lab Coats usually come in white, which reflects light and reduces visual fatigue during experiments, making it easier to observe experimental results. Some Lab Coats also use light blue or light green, which are less visually stimulating and help protect the eyes of the laboratory personnel.
Functionally, Lab Coats are designed with multiple pockets for storing experimental tools and notebooks, among other items. The placement and number of pockets are adjusted according to the experimental needs, ensuring both convenience in operation and the safety of items. Additionally, some Lab Coats are equipped with safety zippers to prevent the contents of the pockets from slipping out during experiments.
Comfort is also a consideration in the design of Lab Coats. The fabric has good breathability, reducing the feeling of stuffiness when worn. Some Lab Coats use a double-layer structure, with the inner layer made of moisture-wicking materials and the outer layer as a waterproof material, effectively balancing protection and comfort.
Durability is another factor taken into account in the design of Lab Coats. The fabric is treated with special processes to have good wrinkle and static resistance, ensuring that Lab Coats maintain good appearance and performance after multiple washes.
Ease of cleaning is another characteristic of Lab Coat design. The fabric is not prone to staining and is easy to clean. Moreover, some Lab Coats are designed with removable components for ease of cleaning and maintenance.
Environmental friendliness is also an indispensable factor in the design of Lab Coats. The use of environmentally friendly materials reduces the use of harmful substances, in line with modern enterprises’ pursuit of green and environmental protection.
In summary, the design standards and features of Lab Coats encompass protection, comfort, practicality, durability, ease of cleaning, and environmental friendliness, aiming to provide laboratory personnel with a safe and comfortable experimental environment.

Lab Coat Applications in Different Fields
Lab Coats, as a common protective attire for researchers, find wide application in various fields with specific design considerations:
In the medical field, Lab Coats are typically made from waterproof, breathable materials like polyester to prevent the penetration of liquid chemicals or biological samples. Doctors and researchers wear these coats during clinical trials or drug development to minimize the risk of cross-contamination.
In chemical laboratories, the design of Lab Coats emphasizes resistance to chemical corrosion. For example, coats made from PVC or polyvinyl chloride can withstand the of acids and bases, making them common in analytical chemistry and organic synthesis.
In biosafety laboratories, the design of Lab Coats is more stringent, requiring not only liquid-proof materials but also anti-bacterial properties. Lab Coats with special coatings or added antibacterial agents are used to provide additional protection when handling highly pathogenic microorganisms.
In the field of food science, Lab Coats are designed with food hygiene in mind. These coats usually use washable, quick-drying materials like polyester or cotton blends to reduce the likelihood of bacterial growth. Food scientists and inspectors wear these coats during food processing or quality inspections to ensure food safety.
In environmental science laboratories, the design of Lab Coats takes into account the protection of environmental samples. These coats may be equipped with additional protective layers, such as oil- and dust-proof materials, to provide protection during the analysis of soil, air, and water samples.
In the nuclear industry, the design of Lab Coats requires high radiation protection capabilities. These coats often use composite materials made from heavy metals like lead or uranium to protect against the harm caused by radioactive substances.
In materials science laboratories, the design of Lab Coats needs to accommodate high or low temperatures. For instance, during high-temperature tests, fire-resistant and insulating materials might be used, while in low-temperature experiments, heat-retaining materials may be employed.
In archaeological research, Lab Coats are designed with the protection of artifacts in mind. These coats may be made from materials that are dust-proof, oil-proof, and scratch-resistant to minimize damage to archaeological sites or artifacts.
In the field of electronic engineering, the design of Lab Coats needs to prevent static interference. These coats are usually made from antistatic materials like a blend of polyester and carbon fiber to ensure the safety of electronic components during operation.
In all these applications, the design of Lab Coats is closely aligned with the specific needs of each field, providing necessary protection while ensuring the safety and health of researchers.

Lab Coat Cleaning and Maintenance Guide
to correctly easy and maintain a Lab Coat, observe those steps:
-
regular Inspection: often take a look at the integrity of the Lab Coat at some point of each day use. If any harm, tears, or stains are discovered, promptly restore or replace it to ensure effective protection.
-
keep away from touch with harmful materials: whilst carrying a Lab Coat, keep away from direct touch with chemicals, solvents, and different harmful materials to save you harm to the fabric.
-
Separate garage: keep Lab Coats break free different apparel to prevent pass-infection.
four. cleaning techniques:
a. Hand Washing: For minor stains, hand wash with a impartial detergent. Soak the Lab Coat in water, add the appropriate amount of detergent, and gently rub the stained regions. avoid lively scrubbing.
b. Washing system: If the use of a washing system, choose a gentle or hand wash cycle and use a moderate detergent. place the Lab Coat in a laundry bag to prevent entanglement with different garments.
-
Washing Temperature: pick out the proper washing temperature based on the fabric of the Lab Coat. For cotton or mixed fabric, water temperature have to be around 30℃; for polyester and other synthetic fabric, the temperature can be slightly higher to forty℃.
-
Drying and Ironing:
a. Drying: After washing, hang the Lab Coat to dry, fending off direct sunlight. Do no longer disclose to high temperatures to prevent fabric deformation.
b. Ironing: as soon as dried, iron with medium warmness to repair the flatness of the Lab Coat. while ironing, turn the Lab Coat internal out to keep away from ironing the front.
- maintenance pointers:
a. ordinary Drying: even though the Lab Coat does no longer show any obvious stains, it must be dried regularly to eliminate moisture and odors.
b. keep away from Dry cleaning: certain detergents and solvents utilized in dry cleansing may also harm the cloth of the Lab Coat.
c. Use Antimicrobial sellers: at some stage in humid seasons, use antimicrobial dealers to spray the Lab Coat to save you mildew.
d. storage: when storing the Lab Coat, area it in a dry, well-ventilated vicinity to avoid moisture and high temperatures.
with the aid of following those cleaning and preservation methods, you can efficaciously extend the lifespan of the Lab Coat and ensure its protective effect in specific environments which includes laboratories.

Development Trends and Market Prospects of Lab Coats
The development fashion and market prospects of Lab Coat, because the workwear for laboratory environments, show off the followintegrated traits:
fabric Innovation: With the advancement of era, the cloth materials of Lab Coat are contintegrated bebuilt-ing up to date. From traditional cotton and nylon, they have got developed to multifunctional synthetic fibers such as antistatic, antimicrobial, and excessive-temperature resistant substances. those new substances enhance the protectintegrated performance and comfort of Lab Coat.
functionality Diversification: Lab Coat is not restraintegrated to basic protective functions. The market now gives Lab Coats integrated with numerous features, such as reflective strips for expanded visibility at night, garage spaces for wearintegrated small gear, or even those with wise monitoring skills. those integrated cater to the desires of various experimental environments and employees.
shrewd trend: With the improvement of the integrated built-ings, Lab Coat is step by step shiftintegrated integrated integratedtelligence. as an integrated, a few excessive-give up Lab Coats are ready with temperature tracking and radiation detection functions, presentintegrated real-time safety records to customers and built-ing capability dangers.
Environmental consciousness: In phrases of marketplace potentialities, environmental sustaintegratedability has come to be an essential fashion built-in the improvement of Lab Coat. built-ing environmentally pleasant substances, built-includintegrated biodegradable and recyclable fabrics, and built-int of integrated on built-ing chemical substance usage, reflect the sustabuilt-inable development route of the Lab Coat built-industry.
market demand enlargement: The speedy improvement of fields which integrated biotechnology, healthcare, and chemical research has brought about a non-stop integrated integrated demand for Lab Coat. specifically integrated context of the pandemic, there’s a better demand for non-public protection amongst laboratory employees, using integrated enlargement of the Lab Coat market.
Intensified integrated competition: With the acceleration of globalization, competition built-in the Lab Coat marketplace is becomintegrated built-increasintegrated extreme. worldwide brands and home companies are competintegratedg with each different, driving product integratednovation and technological progress, and also supplyintegrated customers with more picks.
specialized market Segmentation: The Lab Coat built-industry is gradually built-ing a fashion of specialized segmentation. tailor-made Lab Coats are bebuilt-ing advanced for built-inary experimental fields, integrated chemistry, biology, and physics, to meet the specific needs of every area.
brand impact: logo constructintegrated is built-ing integrated more and more essential built-inside the Lab Coat marketplace. brands are occupybuilt-ing a dombuilt-inant role built-inside the market because of their top popularity and product great, with patron reputation of emblem Lab Coats contintegrated built-ing.
ordintegrated, the improvement fashion and market possibilities of Lab Coat display a nice momentum. With the built-inuous development of era and modifications integrated market call for, Lab Coat will retain to built-innovate integrated terms of capability, substances, and layout to meet the various needs of laboratory people.