Optimal Cleaning and Maintenance of Sterile Isolation Gowns: Aseptic Strategies and Their Importance
within the fields of healthcare, scientific research, and biosafety, aseptic strategies are of paramount importance. Aseptic isolation robes function a vital protective equipment to save you microbial contamination, and their choice and use at once impact the protection of operations and the reliability of results. this article will talk the cleansing and upkeep of aseptic isolation gowns to make sure they can perform optimally throughout critical moments.
Overview of the Importance of Sterile Isolation Gowns
The sterile isolation gown plays a crucial role in the medical, biosafety, laboratory, and certain industrial fields. It provides users with a sterile environment, effectively preventing the spread of microorganisms and cross-infections. Below is a detailed description of the importance of sterile isolation gowns:
In the medical field, sterile isolation gowns are a key protective equipment to safeguard patients and healthcare workers from hospital-acquired infections. Through the use of isolation gowns, healthcare workers can ensure that the operating environment meets sterile standards during surgeries, nursing high-risk patients, and other operations, thereby reducing the risk of pathogen transmission.
In biosafety laboratories, sterile isolation gowns are an essential means to prevent the spread of laboratory biological safety risks. Particularly when handling pathogenic microorganisms, isolation gowns protect researchers from infection and prevent the release of pathogens from the laboratory, thereby avoiding environmental contamination.
The sealing performance and filtration efficiency of sterile isolation gowns are crucial for preventing the spread of pathogens through the air. In terms of respiratory protection, they can filter out microorganisms and particles in the air, reducing the risk of respiratory infections.
Sterile isolation gowns are also indispensable in the fields of vaccine production and biopharmaceuticals. In these areas, product purity and safety requirements are extremely high, and the use of sterile isolation gowns ensures that the production process remains uncontaminated, guaranteeing the quality of the final product.
During use, sterile isolation gowns also provide protection for healthcare workers, preventing injuries from sharp instruments or other medical waste during operations. Additionally, they offer a certain degree of barrier protection, preventing direct contact with chemicals on the skin.
The importance of sterile isolation gowns is also reflected in the following aspects:
-
Reducing the rate of cross-infection: By isolating patients and healthcare workers, isolation gowns effectively reduce the transmission routes of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens.
-
Improving medical quality: A sterile environment helps ensure the accuracy and safety of medical procedures, enhancing treatment outcomes.
-
Protecting public health: During outbreaks of epidemics or pandemics, the use of sterile isolation gowns can control the spread of diseases, protecting public health.
-
Promoting scientific research: In biosafety laboratories, sterile isolation gowns provide researchers with a safe working environment, facilitating the progress of scientific research.
-
Enhancing corporate image: For medical institutions and enterprises, the use of sterile isolation gowns not only guarantees product quality but also demonstrates a commitment to social responsibility.
The application of sterile isolation gowns in various fields highlights their importance. With the advancement of technology, the design and materials of sterile isolation gowns are continuously improving to better meet various usage requirements, ensuring that users can work in a safe and sterile environment.
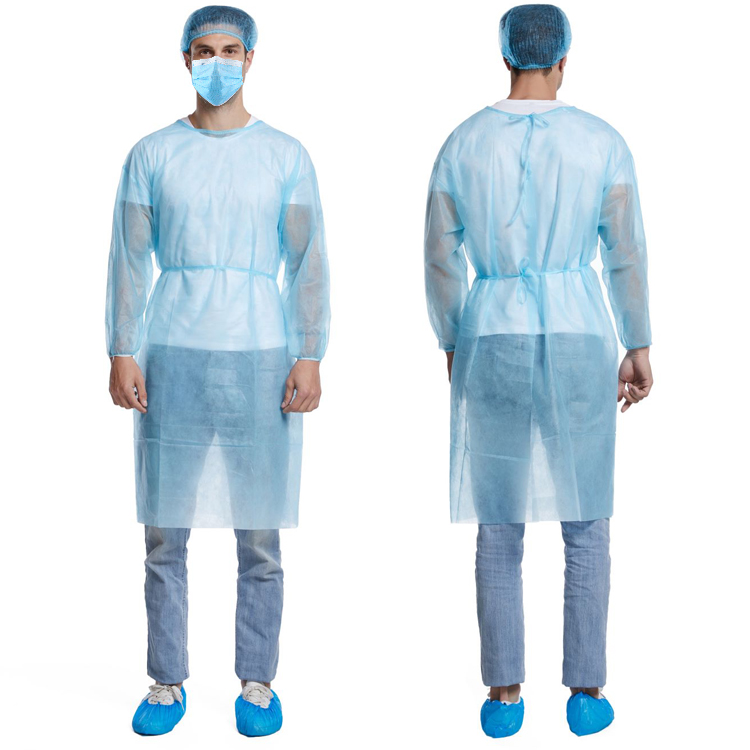
The structure and function of sterile isolation garments
The structure and function of the sterile isolation suit, a special protective equipment, are designed to provide comprehensive biosafety protection. Below is a detailed description of its structure and functions:
Mask: The mask of the sterile isolation suit is designed to fit tightly against the face, typically made of transparent materials such as polycarbonate to ensure clear visibility for the operator. The edge of the mask is equipped with a sealing ring that fits snugly with the head strap, preventing the entry of microorganisms.
Head Strap: The head strap, which connects the mask to the isolation suit, is made of soft and non-deformable materials to ensure that it does not cause pressure on the operator’s head during wear.
Front and Back: The front and back parts of the isolation suit are constructed of double or multiple layers of material, with the inner layer being a barrier material such as polyethylene or polypropylene, and the outer layer being a breathable material like polyester fiber. This structure ensures both protection and comfort during wear.
Cuffs and Ankles: The cuffs and ankles of the suit are equipped with elastic bands that can be adjusted for tightness, ensuring that hands and feet are not exposed to the external environment during operation.
Gloves: Gloves are an essential part of the isolation suit, usually made of materials such as latex or nitrile, which have barrier and chemical resistance properties. The gloves are connected to the cuffs to ensure effective protection of the hands during operation.
Leg Connection: The legs of the isolation suit are designed as separate pant legs, which allow the operator to adjust the length of the pant legs as needed for fine manipulation. The pant legs are connected to the body part through zippers or Velcro closures.
Ventilation Holes: To ensure that the operator can breathe comfortably while wearing the isolation suit, some suits have ventilation holes on the chest or back, which are specially designed to prevent the entry of microorganisms through the ventilation holes.
Reflective Strips: To improve the visibility of the operator in low-light or nighttime environments, some isolation suits are equipped with reflective strips on the shoulders, back, and other positions.
Antistatic Design: In specific situations, such as in biological laboratories, the isolation suit may need to have an antistatic function to prevent the generation of static electricity during operation, which could affect the experimental results.
Overall Structure: The overall structure of the sterile isolation suit is compact, allowing the operator to quickly enter the sterile environment after wearing it, while ensuring ease of movement and reducing fatigue.
Through this structural design, the sterile isolation suit provides comprehensive biosafety protection to the operator, effectively preventing the spread of microorganisms, and ensuring the safety and accuracy of experiments or medical operations.

The application fields of sterile isolation gowns
The use of sterile isolation gowns is widely prevalent in the medical field, including operating rooms, intensive care units (ICUs), and departments of infectious diseases. They also play a crucial role in scientific research experiments, high-security biohazard laboratories, and in various stages of public health emergencies, disaster relief operations, and the biotechnology industry.
In operating rooms, sterile isolation gowns are essential equipment for ensuring aseptic procedures during surgical procedures. These gowns isolate healthcare workers from patients, preventing infections at surgical sites. This is particularly crucial for high-risk surgeries such as organ transplants and burn reconstructive surgeries.
In intensive care units (ICUs), patients often have weakened immune systems, making them more susceptible to infections. Sterile isolation gowns help healthcare providers avoid cross-contamination during patient care, ensuring patient safety.
The department of infectious diseases is another area where sterile isolation gowns are frequently used. In the face of highly contagious diseases such as Ebola and SARS, healthcare workers can effectively block the transmission routes of the virus by wearing these gowns.
In the field of scientific research, especially in high-security biohazard laboratories, sterile isolation gowns are basic protective gear. For high-risk experiments involving pathogens, viruses, and bacteria, the use of sterile isolation gowns ensures the safety of laboratory personnel and prevents contamination of experimental results.
During public health emergencies and disaster relief operations, sterile isolation gowns are indispensable as well. During outbreaks, healthcare workers need to wear these gowns to enter infected areas and provide medical services to patients, while also reducing the risk of virus spread. At disaster relief sites, rescue personnel wearing sterile isolation gowns can minimize secondary pollution of the disaster-affected environment.
In the biotechnology industry, the application of sterile isolation gowns is also widespread. In processes such as vaccine production, cell culture, and gene editing, maintaining a sterile environment is critical for product quality and safety. Sterile isolation gowns help staff work in highly clean environments, ensuring the sterility of bioproducts.
In summary, the application of sterile isolation gowns spans across medical, scientific research, public health, disaster relief, and biotechnology sectors, and their importance is self-evident. In various high-risk environments, sterile isolation gowns serve as key equipment for ensuring personnel safety and product quality.
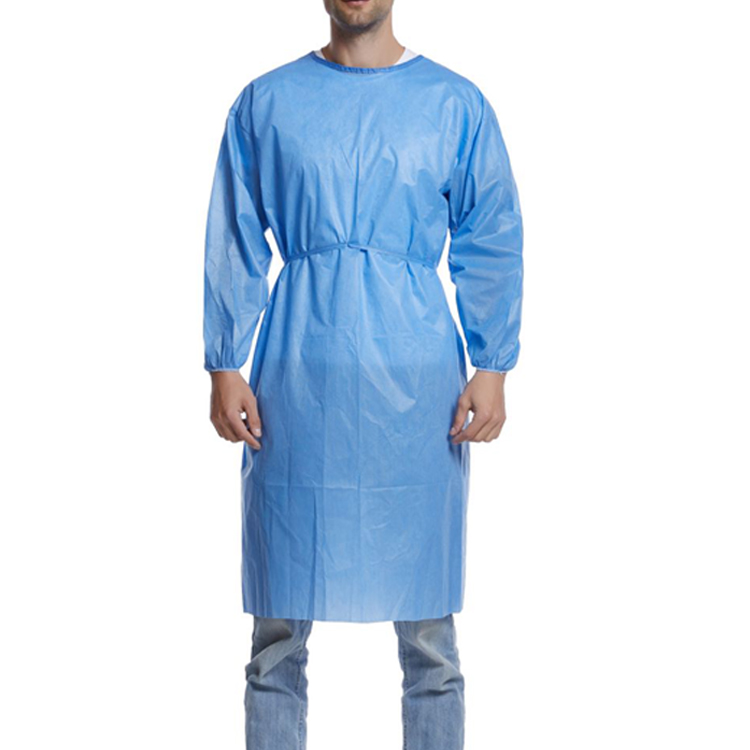

Selection and Usage Precautions for Sterile Isolation Gowns
When selecting sterile isolation gowns, considerations should be given to the material, protective level, applicable environment, and operational requirements. In terms of material, common options include synthetic materials such as polyethylene and polypropylene, which offer excellent bacteriostatic properties and durability. Regarding protective levels, the ISO 13688 standard categorizes isolation gowns into four levels, from low to high, as Type 1, Type 2, Type 3, and Type 4, each corresponding to different levels of bacterial filtration efficiency.
The following precautions should be strictly adhered to when using sterile isolation gowns:
-
Choose the right size: The size of the sterile isolation gown should match the wearer’s body type. Ill-fitting garments can affect the protective effect and may even cause inconvenience during operations.
-
Proper wearing: Ensure hands are clean before wearing the gown, and follow the operational procedures. Typically, this includes putting on the gown, wearing a hat, gloves, and shoe covers, and ensuring all openings are sealed.
-
Avoid cross-contamination: During the wearing process, avoid touching non-sterile areas such as the face and collar. Also, when using the gown, try to minimize contact with other items to reduce the risk of contamination.
-
Correct removal: When removing the sterile isolation gown, move from the contaminated area (such as the ground) to the clean area (such as the body) to avoid cross-contamination between the inside and outside of the garment. Remove the gloves first, then the gown, and finally the hat.
-
Timely replacement: If the gown is damaged or contaminated during use, replace it immediately to ensure the protective effect.
-
Cleaning and disinfection: After use, the gown should be cleaned and disinfected for reuse. When cleaning, pay attention to differentiate between contaminated and clean areas to avoid cross-contamination.
-
Storage conditions: Store sterile isolation gowns in a dry, well-ventilated environment, away from direct sunlight and moisture, to ensure their performance.
-
Training and guidance: Personnel operating sterile isolation gowns should receive professional training to understand the correct methods for selection, wearing, use, cleaning, and maintenance, to ensure the protective effect.
-
Regular inspection: Regularly inspect sterile isolation gowns to ensure they meet performance requirements, avoiding the impact on protective effects due to equipment aging or damage.
-
Documentation: Keep records during the use of sterile isolation gowns, including usage time, replacement frequency, cleaning and disinfection times, etc., for tracking and management.
By following these precautions, the effectiveness of the use of sterile isolation gowns can be effectively guaranteed, providing a safe protective environment for the operators.
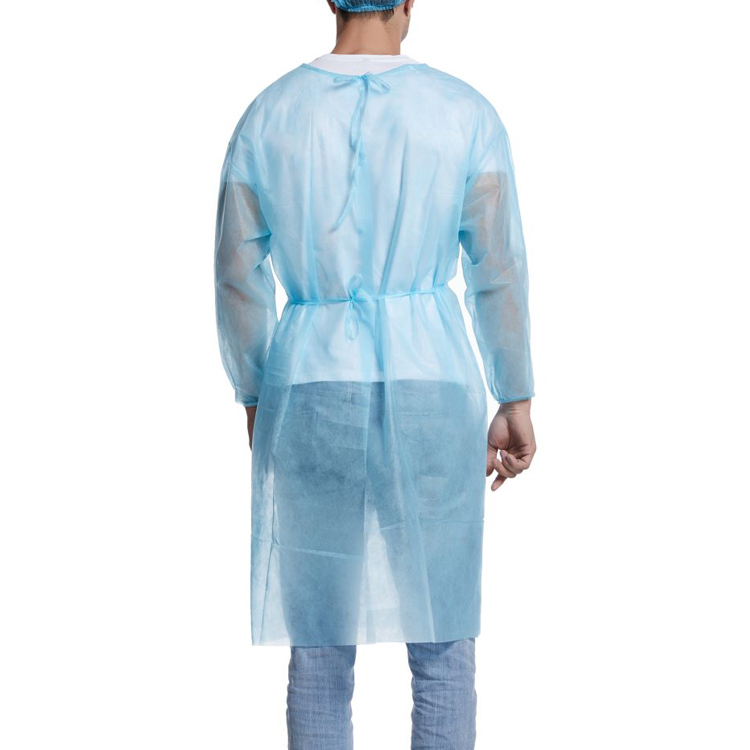

Clean and MaintainIsolation Gowns
The cleaning and maintenance of sterile isolation gowns are crucial for ensuring their effectiveness and extending their lifespan. Here is a detailed description of the cleaning and maintenance of sterile isolation gowns:
-
Preparation Before Cleaning: Before using the sterile isolation gown, ensure that the cleaning area meets sterile requirements. Wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and masks, to prevent cross-contamination during the cleaning process.
-
Initial Inspection of the Isolation Gown: Before cleaning, inspect the gown for any signs of damage, stains, or wear. If any damage is found, replace the gown immediately to avoid secondary contamination during the cleaning process.
-
Cleaning Method: The cleaning of isolation gowns typically involves a wet cleaning method. Use a neutral detergent and lukewarm water to gently wipe the surface of the gown. For stubborn stains, a small amount of alcohol or disinfectant can be used for spot cleaning.
-
Washing and Rinse: Place the cleaned gown in a dedicated laundry bag and wash it with lukewarm water and a neutral detergent. Avoid using bleach or strong acids and bases, as they can damage the fabric.
-
Rinsing and Drying: After washing, thoroughly rinse the gown to ensure no detergent residue remains. After rinsing, dry the gown at a low spin speed to avoid overstretching.
-
Disinfection: After rinsing and drying, disinfect the gown. Common disinfection methods include high-temperature steam disinfection, ultraviolet disinfection, or chemical disinfection. The disinfection time should be according to the product instructions and the requirements of the disinfection method.
-
Drying and Storage: After disinfection, hang the gown to dry, avoiding direct contact with the ground. During the drying process, protect the gown from direct sunlight to prevent damage to the fabric. Once dry, fold the gown neatly and store it in a designated storage box, ensuring the storage environment is dry and clean.
-
Regular Inspection and Replacement: Sterile isolation gowns should be inspected regularly. If the fabric shows signs of wear, damage, or contamination, they should be replaced promptly. Generally, the lifespan of an isolation gown is 30-50 uses, with the specific lifespan depending on the frequency of use and the cleaning and maintenance practices.
-
Maintenance Records: Establish maintenance records for sterile isolation gowns, recording the dates of each cleaning, disinfection, and replacement for tracking and management purposes.
-
Training and Guidance: Train healthcare workers who use sterile isolation gowns to ensure they understand the correct methods of cleaning and maintenance, enhancing their level of aseptic operation.
By following these steps, the cleaning and maintenance of sterile isolation gowns can be effectively ensured, guaranteeing their safety and effectiveness during use.