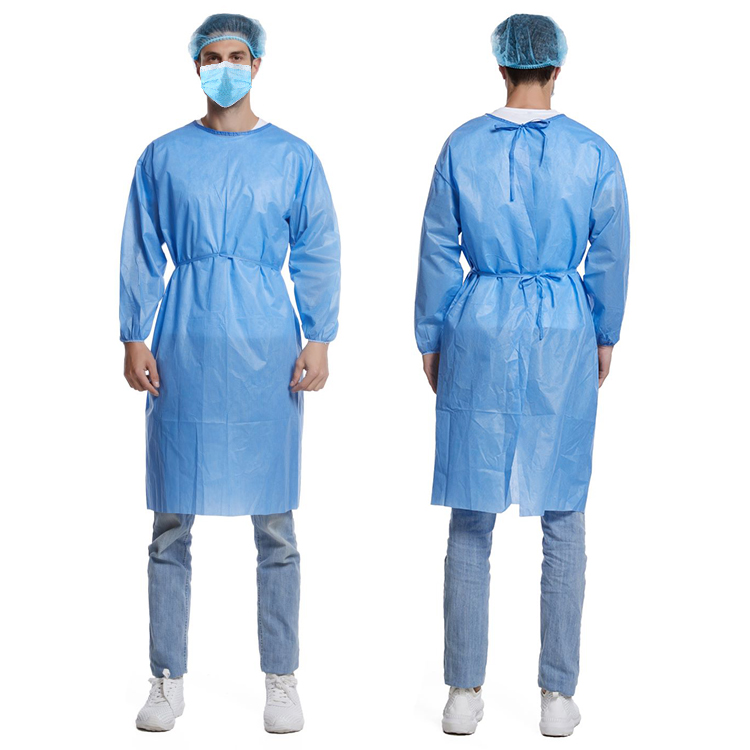
Protective Fabric It: x, q, with Comprehensive Guide and Market Trends
In today’s rapidly evolving industrial and daily life, protective fabrics serve as crucial materials for safety and hygiene, and their applications are increasingly widespread. This article will discuss the material characteristics of protective fabrics, guidelines for selection and use, as well as the challenges faced by current market trends.
Protective
Protective fabrics are a widely used functional material in various fields such as industry, healthcare, and construction. They are mainly made from synthetic fibers or natural fibers, and possess excellent properties such as wear resistance, dustproofing, waterproofing, and oil resistance, playing a crucial role in ensuring human safety and environmental cleanliness.
There are many types of protective fabrics, including but not limited to the following:
-
Disposable Protective Fabrics: Suitable for places like hospitals and laboratories, these fabrics can effectively isolate pathogenic microorganisms and pollutants, ensuring the hygiene and safety of the working environment.
-
High-Temperature Protective Fabrics: Used in high-temperature work environments such as welding and forging, these fabrics provide necessary insulation and fire protection.
-
Dustproof Protective Fabrics: Widely used in industrial production and mining operations, these fabrics prevent dust and particulate matter from polluting the environment and harming human health.
-
Oilproof Protective Fabrics: Used in places like catering and kitchens, these fabrics effectively prevent oil from spilling and spreading, maintaining cleanliness and hygiene.
-
Anti-Static Protective Fabrics: Suitable for environments prone to static electricity, such as electronics assembly and petrochemical industries, to prevent static from affecting equipment and products.
The performance indicators of protective fabrics mainly include:
-
Strength: Refers to the tensile and tear strength of the fabric, ensuring that it is not easily damaged during use.
-
Breathability: Refers to the air permeability of the fabric, affecting comfort during wearing.
-
Barrier Properties: Refers to the fabric’s ability to block harmful substances such as moisture, oil, and bacteria.
-
Flame Retardancy: Refers to the fabric’s resistance to combustion under the action of a flame, reducing the risk of fire.
-
Chemical Resistance: Refers to the fabric’s resistance to acidic, alkaline, and solvent chemicals.
When selecting and using protective fabrics, the following factors should be considered:
-
Usage Environment: Choose the appropriate protective fabric based on the specific environment of the workplace.
-
Protection Needs: Select protective fabrics with the corresponding protective properties based on actual needs.
-
Cost-Effectiveness: Consider the price and performance of the protective fabric to choose a cost-effective product.
-
Maintenance and Care: Understand the cleaning, disinfection, and maintenance methods of the protective fabric to extend its service life.
With the increasing awareness of environmental protection, protective fabrics are paying more attention to the application of environmentally friendly materials and processes, such as biodegradable materials and non-woven fabrics. At the same time, new types of protective fabrics are emerging to meet the diverse market demands. In the future, protective fabrics will continue to play an important role in ensuring human safety and environmental cleanliness.

Application fields of protective fabric
Protective fabrics play a crucial role in various industries, with their applications spanning a wide range of fields, including:
-
Healthcare: In medical settings, protective fabrics are used in isolation wards, operating rooms, and other areas to prevent cross-infection. They cover bedding, mattresses, and are used in sterile procedures for surgical personnel.
-
Construction: On construction sites, protective fabrics are used to shield workers from falling objects from heights and to prevent dust from spreading, contaminating the environment. Construction hoarding and temporary covering materials often utilize protective fabrics as well.
-
Automotive Manufacturing: In automotive manufacturing, protective fabrics are used to isolate different assembly areas, ensuring that components are not contaminated during specific processing and that the ground is not polluted by oil spills.
-
Environmental Protection: In the environmental sector, protective fabrics are used for handling solid waste, covering landfill sites, and preventing leakage in wastewater treatment plants.
-
Warehousing and Logistics: In warehousing and logistics, protective fabrics are used to cover goods, preventing them from getting wet or contaminated, and facilitating their protection during transportation.
-
Agricultural Production: In agricultural activities, protective fabrics are used in greenhouses and greenhouses to provide insulation, pest control, and shading, which help to increase crop yield and quality.
-
Transportation: In the transportation sector, protective fabrics are used for ship leak prevention, corrosion protection, and to safeguard goods during vehicle transportation.
-
Energy Industry: In the energy industry, protective fabrics are used to prevent oil and gas leakage and to protect equipment from adverse weather conditions.
-
Military Field: In military facilities and training exercises, protective fabrics are used to construct temporary shelters, providing cover and protection.
-
Daily Necessities: Items like shopping bags, garbage bags, raincoats, and more in everyday life also fall under the category of protective fabrics, catering to daily protective needs.
The extensive range of applications for protective fabrics not only demonstrates their versatility but also highlights their significant value in protecting human health, environmental protection, and production safety. With the advancement of technology, new types of protective fabric materials are constantly emerging, and their future prospects for application in various fields will be even broader.

Material and Properties of Protective Fabrics
The protective fabrics are widely used in various materials, each with its unique characteristics and applications. The following is a description of several common protective fabric materials and their properties:
-
Polyethylene (PE)Polyethylene material protective fabrics have excellent corrosion resistance, acid and alkali resistance, and aging resistance. They are lightweight, soft, easy to fold and carry, and are commonly used in construction sites, home renovations, and agricultural fields, such as covering crops to protect against pests and rain.
-
Polypropylene (PP)Polypropylene material protective fabrics have high strength and tear resistance, as well as good heat and cold resistance. They are widely used in outdoor shading, tent making, and industrial packaging fields.
-
PVC (Polyvinyl Chloride)PVC material protective fabrics have excellent waterproof, oil-proof, and chemical corrosion resistance. They are durable, easy to clean, and commonly used in medical, catering industries as isolation and protective materials, as well as for outdoor billboards and temporary constructions.
-
NylonNylon material protective fabrics are known for their excellent strength and wear resistance, as well as good UV resistance. They are commonly used in outdoor sports equipment, life jackets, tents, and various protective fabric products requiring high strength.
-
Cotton FabricCotton fabric protective fabrics have good breathability and moisture absorption, suitable for use as summer shading, sun protection, and decorative fabrics. They are harmless to the human body and suitable for family, parks, and other leisure places.
-
CanvasCanvas material protective fabrics have strong durability, good wind resistance, and waterproof performance. They are commonly used for tents, shading canopies, outdoor furniture covers, and so on.
-
Nonwoven FabricNonwoven fabric materials are light, soft, and have good environmental protection properties. They are commonly used in disposable medical supplies, household items, and industrial packaging fields.
-
Fireproof FabricFireproof fabrics are made of special fibers and have flame-retardant or non-flammable properties, suitable for occasions requiring fire prevention, such as theaters, shopping malls, and warehouses.
-
Conductive FabricConductive fabrics contain conductive fibers and can effectively shield electromagnetic interference, commonly used in the anti-static packaging of electronic devices and shielding covers.
-
Insulation FabricInsulation fabrics are made of high-reflectivity materials and have good insulation and thermal insulation properties. They are suitable for insulation and thermal insulation projects, as well as for cold chain logistics.
These materials of protective fabrics have different focuses on performance, and selecting the appropriate material based on different application requirements and occasions can maximize the effectiveness of the protective fabrics.

Guide for Choosing and Using Protective Fabrics
When selecting protective fabrics, considerations should be given to their intended use, environment, and materials they will come into contact with. Here are some guidelines for choosing and using protective fabrics:
- Selecting Based on Purpose
- Dustproof Fabric: Suitable for industrial production, construction sites, and other places where dust control is necessary.
- Waterproof Fabric: Used for outdoor activities and temporary constructions, offering excellent waterproof properties.
- Oilproof Fabric: Ideal for kitchen and restaurant environments prone to oil stains, easy to clean.
- Antimicrobial Fabric: Appropriate for medical and laboratory settings with high hygiene requirements, providing antimicrobial properties.
- Considering Material Characteristics
- Polyethylene (PE): Lightweight, waterproof, and corrosion-resistant, suitable for various applications.
- Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC): Resistant to oil and chemicals, suitable for environments with contact with oils and chemicals.
- Nonwoven Fabric: Soft and breathable, suitable for medical care, food packaging, and other fields.
- Nylon: Abrasion-resistant and heat-resistant, suitable for special industrial uses.
- Size and Shape
- Choose the appropriate size of the protective fabric based on the protected area.
- Custom shapes, such as square, rectangular, or circular, can be made to meet different needs.
- Installation and Fixing
- Lay the protective fabric flat to avoid wrinkles.
- Use fasteners, hooks, and other tools to ensure the fabric is securely fixed.
- Cleaning and Maintenance
- Clean the protective fabric regularly to maintain its cleanliness and effectiveness.
- Avoid using corrosive chemicals such as strong acids or alkalis when cleaning.
- Choose appropriate cleaning agents and methods based on the material characteristics.
- Replacement Cycle
- Observe the wear of the protective fabric and replace it in a timely manner.
- For protective fabrics exposed to harsh environments for a long time, the replacement cycle should be shortened.
- Precautions
- Avoid exposing the protective fabric to direct sunlight for extended periods to prevent aging.
- Be careful to avoid sharp objects that could damage the protective fabric during use.
- Store the fabric in a dry place to prevent mold due to moisture.
By following these guidelines, users can select the appropriate protective fabric based on their actual needs, ensuring it performs optimally during use and extends its lifespan.
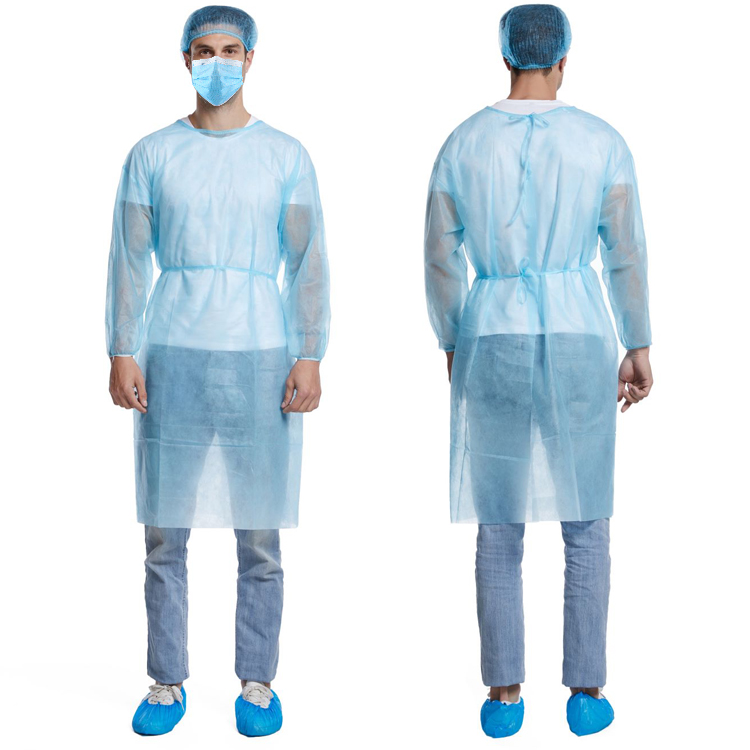
Market Trends and Challenges of Protective Fabric
The protective fabric market is experiencing rapid changes, with the following notable trends and challenges:
Material Innovation: With the advancement of technology, new protective fabric materials are continuously emerging. For example, nanocoating technology has enabled protective fabrics to have more efficient waterproof, oil-proof, and antibacterial properties, meeting higher performance requirements from various industries.
Increased Environmental Awareness: Amid global environmental trends, sustainability has become an important consideration in the protective fabric market. Biodegradable materials and recyclable materials as eco-friendly protective fabrics are gaining popularity, driving the industry towards a greener and lower-carbon direction.
Customization: With the widespread of customized services, the protective fabric market is also moving towards customization. Different industries and scenarios have varying demands for protective fabrics, and companies need to provide diverse designs and services to meet specific customer needs.
Intensified Market Competition: As more and more enterprises enter the protective fabric market, competition is becoming increasingly fierce. Price wars and homogenized products are the norm, and companies need to enhance their competitiveness through technological innovation and brand building.
Supply Chain Management Challenges: Factors such as fluctuating raw material prices and rising logistics costs pose challenges to the supply chain management of protective fabrics. Companies need to optimize their supply chains, reduce costs, and ensure product quality and delivery times.
Changes in Regulations and Standards: Strict requirements for the production and sale of protective fabrics vary by country and region. Companies need to closely monitor regulatory dynamics to ensure their products comply with relevant standards and avoid potential legal risks.
Technological Updates and Iterations: The application of new technologies is continuously improving the performance of protective fabrics. New products such as smart protective fabrics and multifunctional composite fabrics are constantly being introduced, and companies need to keep up with technological trends and continue to innovate.
Diverse Customer Needs: Different industries and scenarios have varying requirements for the functions, appearance, and dimensions of protective fabrics. Companies need to have flexible response capabilities and quickly adjust their production strategies to meet diverse customer demands.
Market Expansion and Internationalization: With the acceleration of globalization, the protective fabric market is gradually expanding into international markets. Companies need to consider cross-cultural differences and establish international sales networks and service systems.